How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced flight techniques and legal considerations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, camera operation, and troubleshooting, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the skies.
Understanding the fundamental principles of drone flight, including navigation, control inputs, and various flight modes, is crucial for safe and efficient operation. We will delve into the importance of adhering to local regulations and airspace restrictions, ensuring responsible and legal drone usage. Furthermore, this guide will provide practical advice on maintaining your drone and troubleshooting common issues, maximizing its lifespan and performance.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, verifying battery levels, and confirming adherence to local regulations. Understanding and respecting airspace restrictions and safety precautions are paramount to responsible drone piloting.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection should be performed before every flight. This minimizes the risk of malfunctions and ensures the drone is in optimal condition.
| Item | Check | Action Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage or cracks | Replace damaged propellers | Ensure all propellers are securely fastened. |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition | Charge battery if necessary; replace if damaged | Use only manufacturer-approved batteries. |
| Gimbal | Check for smooth movement and proper alignment | Adjust or recalibrate if necessary | Ensure the gimbal is securely mounted. |
| Camera | Check lens for cleanliness and proper function | Clean lens if necessary; troubleshoot if malfunctioning | Ensure the camera is securely attached. |
| GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception if necessary | Sufficient satellites are required for stable flight. |
| Flight Controller | Verify proper functionality | Perform a calibration if needed | Ensure the flight controller is functioning correctly. |
| Remote Controller | Check battery level and connection | Charge if necessary; troubleshoot connection issues | Ensure proper connection between controller and drone. |
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone requires understanding and adhering to local regulations. These regulations vary by location and often include restrictions on flight altitude, proximity to airports, and areas of restricted airspace. Familiarize yourself with the specific regulations in your area before flying.
Safety Precautions for Various Environments
Safety precautions vary depending on the environment. Urban environments require extra caution due to obstacles and people. Rural areas may present challenges like uneven terrain and wildlife. Near water, always be prepared for potential water landings.
- Urban Areas: Maintain a safe distance from buildings, people, and vehicles. Avoid flying over crowds.
- Rural Areas: Be aware of uneven terrain, obstacles, and wildlife. Check for potential hazards before takeoff.
- Near Water: Always have a backup plan in case of a water landing. Consider using flotation devices for your drone.
Safe Flight Conditions Decision-Making Flowchart

A flowchart helps visualize the decision-making process for determining safe flight conditions. This ensures that all necessary factors are considered before commencing flight.
[Illustrative description of a flowchart. The flowchart would start with “Is the weather suitable?” branching to “Yes” (proceed to pre-flight checks) and “No” (abort flight). The “Yes” branch would lead to further checks such as “Is the GPS signal strong?”, “Are there any airspace restrictions?”, and “Are there any obstacles?”. Each check would have a “Yes” (proceed) and “No” (abort) branch.
The final decision would be “Safe to fly?” with “Yes” leading to takeoff and “No” leading to abort flight.]
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and efficient operation. This section details the basic controls, different control methods, GPS navigation, and a step-by-step guide for takeoff, hovering, and landing.
Basic Drone Controls
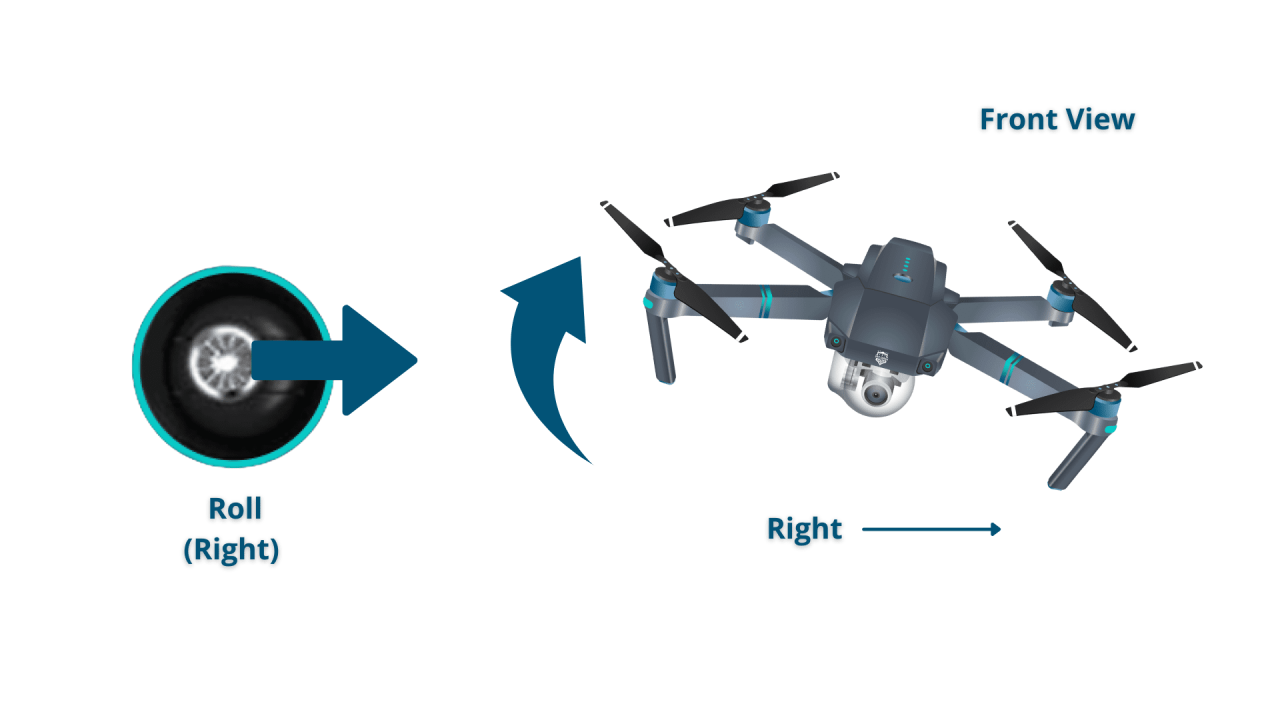
Most drones use four primary controls: throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. Understanding these controls is fundamental to piloting.
- Throttle: Controls altitude (up and down).
- Yaw: Controls rotation (left and right).
- Pitch: Controls forward and backward movement.
- Roll: Controls side-to-side movement.
Drone Control Methods
Drones can be controlled using joysticks or app-based controls. Joysticks offer more precise control, while app-based controls provide a more intuitive interface, often better suited for beginners.
GPS Navigation
GPS navigation is crucial for precise positioning and autonomous features. It allows the drone to maintain its location and return to its starting point. Accuracy depends on GPS signal strength and satellite availability.
Safe Takeoff, Hovering, and Landing
A smooth takeoff, stable hover, and safe landing are crucial for successful drone operation. This step-by-step guide will Artikel the procedure.
- Pre-flight checks: Complete all pre-flight checks.
- Takeoff: Gently increase throttle to lift the drone off the ground.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position by carefully adjusting the throttle and other controls.
- Navigation: Use the controls to maneuver the drone as needed.
- Landing: Gradually decrease throttle to lower the drone to the ground.
Flight Modes and Features
Modern drones offer various flight modes and advanced features that enhance safety, control, and creative possibilities. Understanding these modes and features is key to maximizing your drone’s potential.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight situations. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode allows for more aggressive maneuvers.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness for easier control.
- Sport Mode: Enables faster speeds and more agile maneuvers.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for precise positioning and autonomous features.
Advanced Drone Features
Advanced features enhance safety and creative capabilities. Obstacle avoidance prevents collisions, while return-to-home ensures a safe landing even if the signal is lost.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Uses sensors to detect and avoid obstacles.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point.
- Follow Me: The drone automatically follows a designated subject.
Autonomous Flight Features: Benefits and Limitations
Autonomous flight features offer convenience and creative possibilities but have limitations. While simplifying operation, they still require careful monitoring and understanding of their limitations.
Comparison of Flight Modes
| Flight Mode | Capabilities | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limited speed, stable flight | Beginners, calm conditions |
| Sport Mode | High speed, agile maneuvers | Experienced pilots, open spaces |
| GPS Mode | Precise positioning, RTH | Various tasks, requiring precise positioning |
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography
The camera is a key feature of most drones. Understanding camera settings and techniques is crucial for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Optimal image quality requires adjusting camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture. These settings interact to affect exposure, depth of field, and motion blur.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light (higher ISO for low-light conditions).
- Shutter Speed: Controls the duration the shutter is open (faster shutter speed for freezing motion).
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening (wider aperture for shallower depth of field).
Capturing Different Types of Shots, How to operate a drone
Drones allow for creative aerial shots like panoramas, time-lapses, and cinematic footage. Each shot requires specific techniques and planning.
- Aerial Panoramas: Capture a wide-angle view by stitching multiple photos together.
- Time-lapses: Capture the change over time by taking photos at intervals.
- Cinematic Footage: Use smooth movements and creative angles to create visually appealing videos.
Composing Effective Drone Shots
Effective composition involves considering the rule of thirds, leading lines, and the overall visual balance of the shot. Planning the shot beforehand is crucial.
Editing Drone Footage
Basic video editing software allows enhancing drone footage. This involves cutting, color correction, and adding transitions.
- Import Footage: Import the drone footage into your editing software.
- Cutting and Trimming: Remove unwanted sections of the footage.
- Color Correction: Adjust the colors to enhance the mood and look.
- Adding Transitions: Use transitions to create a smooth flow between different clips.
- Adding Music and Sound Effects: Enhance the mood and engagement of the video.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its optimal performance. This section covers common problems and their solutions, along with best practices for storage and maintenance.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Several common issues can affect drone operation. Understanding these issues and their solutions is crucial for efficient troubleshooting.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to enhance your skills and ensure safe flights.
Proper training is crucial before operating any drone, ensuring both personal safety and responsible use of this technology.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully before each flight. Consider carrying spare batteries.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with better GPS reception.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motors for damage and replace if necessary.
- Gimbal Issues: Recalibrate the gimbal or contact support for assistance.
Drone Storage and Maintenance
Proper storage and maintenance extend the life of your drone. This includes keeping it clean, dry, and stored in a protective case.
Calibration and Firmware Updates
Regular calibration ensures the drone’s sensors are properly aligned, while firmware updates improve performance and address bugs.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
[Illustrative description of a flowchart. The flowchart would start with “Drone Problem?”. Branches would lead to specific problems like “Low Battery?”, “GPS Signal Loss?”, “Motor Malfunction?”. Each problem would have a corresponding solution and potential next steps. The flowchart would guide users through a series of troubleshooting steps until the problem is resolved or further assistance is needed.]
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Responsible drone operation involves understanding and adhering to legal requirements and ethical considerations. This section covers legal aspects, ethical implications, and resources for further information.
Legal Requirements for Drone Operation
Drone laws and regulations vary widely by region. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific regulations in your area before flying.
Ethical Considerations in Drone Use
Ethical considerations involve respecting privacy, avoiding intrusive surveillance, and ensuring safe operation. Responsible drone piloting prioritizes the safety and well-being of others.
Responsible Drone Operation and Privacy
Responsible drone operation emphasizes respecting others’ privacy and avoiding potentially harmful or intrusive actions. This includes refraining from filming people without their consent.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering the art of drone operation requires practice and patience, but the rewards of capturing stunning aerial footage are well worth the effort.
Resources for Drone Laws and Regulations

Several resources provide information on drone laws and regulations. These resources can help you stay informed and ensure compliance.
- Local aviation authorities
- National aviation authorities
- Drone industry associations
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with a responsible approach to flight. By understanding the principles of safe flight, adhering to regulations, and employing best practices for maintenance and troubleshooting, you can unlock the full potential of your drone. Remember, responsible drone operation is not just about technical proficiency; it’s about ensuring the safety of yourself, others, and the environment.
Continue to learn and practice to become a confident and responsible drone pilot.
Quick FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a GPS-equipped drone with beginner mode and return-to-home functionality is recommended. These features offer added safety and simplify operation.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibrating your drone’s compass and IMU should be done before each flight, especially after a crash or significant impact. Refer to your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
What is the maximum flight time for most drones?
Flight times vary significantly depending on the drone model and battery size. Expect anywhere from 15-30 minutes on a single charge for most consumer drones.
Can I fly my drone in the rain?
No, most drones are not waterproof and should not be flown in rain or other wet conditions. Doing so can damage the electronics.
